Abstract
现存的语义分割方法都依赖于大量的特征以及邻域点之间的相互作用,无法发挥他们的潜力。本文提出一个基于CNN的提取高级特征的方法。提出一种将3d点云邻域的特征转化为2d图像的方法。首先,在一个窗口内对每一个点提取他们的局部几何特征、全局几何特征、全波形特征并把特征转为2D图像。然后使用这个生成的图像作为CNN的输入,实现3D语义分割的任务。最后使用ISPRS的数据集进行评估,OverAll可达到82.3。
# A Convolutional Neural Network-Based 3D Semantic Labeling Method for ALS Point Clouds
Zhishuang Yang, Wanshou Jiang ,*ID , Bo XuID , Quansheng Zhu , San JiangID and Wei Huang
State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping and Remote Sensing,
Abstract
现存的语义分割方法都依赖于大量的特征以及邻域点之间的相互作用,无法发挥他们的潜力。本文提出一个基于CNN的提取高级特征的方法。提出一种将3d点云邻域的特征转化为2d图像的方法。首先,在一个窗口内对每一个点提取他们的局部几何特征、全局几何特征、全波形特征并把特征转为2D图像。然后使用这个生成的图像作为CNN的输入,实现3D语义分割的任务。最后使用ISPRS的数据集进行评估,OverAll可达到82.3。
1. Introduction
简单介绍之前的机器学习方法,机器学习方法最大的缺点就是不考虑邻域点的label信息(上下文信息)独立地对每一个点进行分类。因此引入了MRF和CRF以获得各类之间的依赖。
我们提出了一种根据单点生成特征图像的方法。使用局部几何特征、全局几何特征、全波形特征从邻域点生成特征图像。
2. Methodology
工作流程
首先,我们将点的分类转换为相应特征图像的分类。然后训练。最后使用模型进行分类。
2.1 CNN

完整的公式如下,
卷积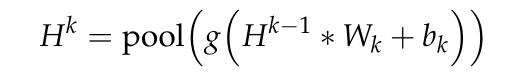
全连接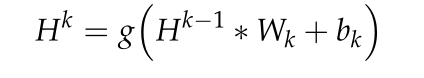
2.2 Feature Image Generation
将点云分成128*128个cell,计算每一个cell的中心坐标。
对每一个cell的中心坐标给定一个固定的半径r,查找其邻域,在其邻域内计算局部几何特征,包括平面性、各向同性、以及法向量和垂直方向之间的角度方差。
使用软件包SCOP++生成DTM并计算Height above.(应该是归一化高程),使用该特征可以区分道路和房顶。
使用全波形雷达特征中的回波强度特征。(The chosen echo intensity values are high on building roofs, on gravels roads, and on cars, while low values are asphalt roads and tar streets [6], which makes these objects easy to distinguish.)
再计算以上特征后,根据特征计算三通道值,
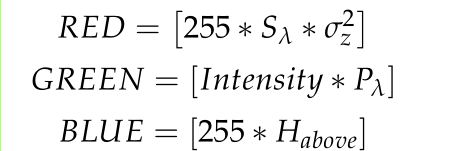
对每一个cell,将根据三通道值赋予颜色rgb,开始的square window就变成了128*128的图像。
这样点的空间语义信息就借助于三种特征转变为了一个图像。CNN模型通过这些有限的低级特征图像提取高级表示。
2.3 Accuracy Evaluation
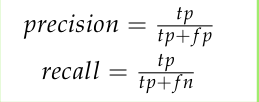

3. Experimental Result
3.1 Dataset
ISPRS 3D数据集。 contains the spatial XYZ-coordinates, intensity values,the number of returns, and the reference labels.
3.2. Experiments
对于每一类的点的数量差距过大,进行了class re-balancing
The batch gradient descent with a batch size of 128 examples, base learning rate of 0.01,momentum of 0.9, and weight decay of 0.0005 to estimate the CNN parameters is used for training。
用5个features和set the width of cell 0.05 m来考虑不同半径的球状邻域的影响

- 用5个features和set the neighborhood radius to 1 m来考虑cell width 的影响

- 最后,选择radius = 1,cell width = 0.05m来考虑5个特征的影响。
不同的选择如下图,

对应的结果如下表,

最终的CNN_DEIV方法分类结果如下,

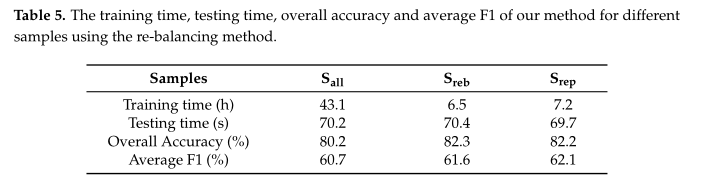
- We use all five features and set the neighborhood radius to 1 m, set the cell width to 0.05 m, and then change the training samples
不同选择如下图,

结果如下表,
3.3 ISPRS Benchmark Testing Results
不同结果的分类结果如下表,

4. Discussion
There are three main parameters in our work: the neighborhood radius, the cell width, and the feature selection.
分析了各个参数的选择过程,发现我们方法的效果很大程度上依赖于DTM的质量(Thus, we may state that the performance of the proposed method depends significantly on the quality of the DTM).
我们的方法效果很好( overall accuracy of our method is ranked 1st, average F1 of the five main categories is ranked 2nd),并且我们的方法仅仅使用了5个特征。另外,特征的数量可能导致了一些误分类(the low quantities of the features may lead to some misclassifications,such as the powerline, fence/hedge and shrubs have relatively low F1 scores.)。选择一些其他特征(高程方差、回波特征、点密度、hierarchical features )或者在邻域选择阶段采用基于熵最大化的方法(eigen-entropy maximization)可能会提高精度。
在我们的框架中,一些非常接近的点会有相同的特征图。尽管考虑了点的空间相关性但仍有一些误分类的点。对每一个点生成特征图耗时、耗资源,可以参考 Guninard [39] [Weakly supervised segmentation-aided classification of urban scenes from 3D lidar point clouds] ,采用一种pre-segmentation的方法减少计算负担。该方法应对了噪声并且减少了特征图的数量。
5. Conclusions
从邻域选择、增加特征、采用segment-based method三个方面提出了改进,以提高精度,减少计算负担。
本文链接: https://suyunzzz.github.io/2020/04/15/【论文阅读】- 2017-A Convolutional Neural Network-Based 3D Semantic Labeling Method for ALS Point Clouds/
版权声明: 本作品采用 知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际许可协议 进行许可。转载请注明出处!



